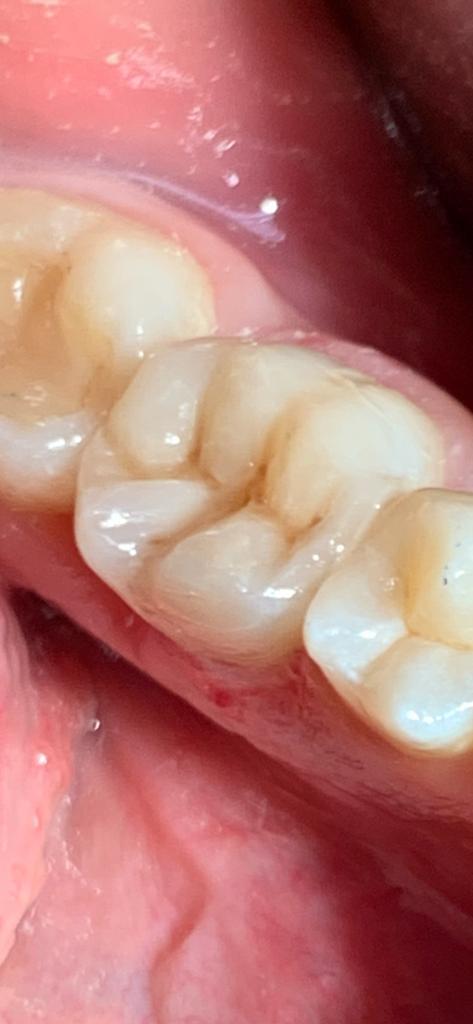
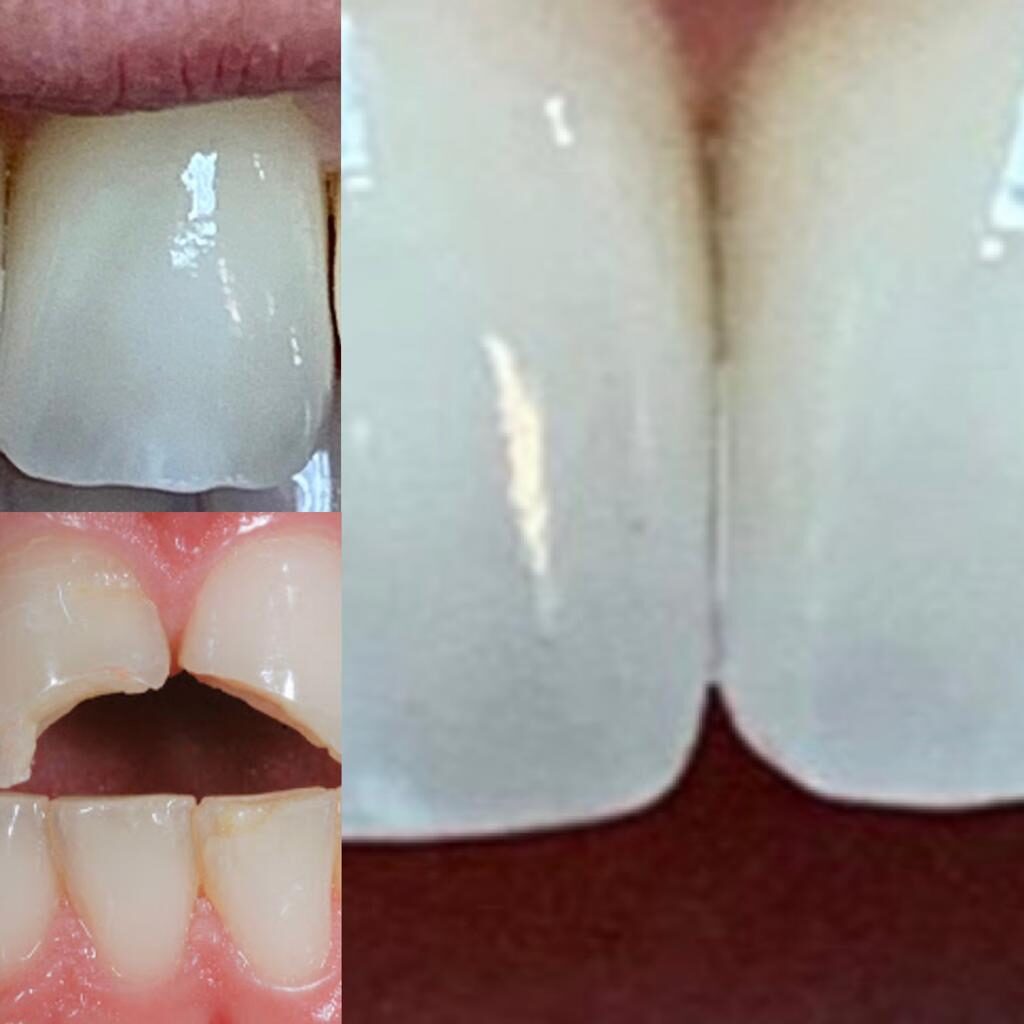
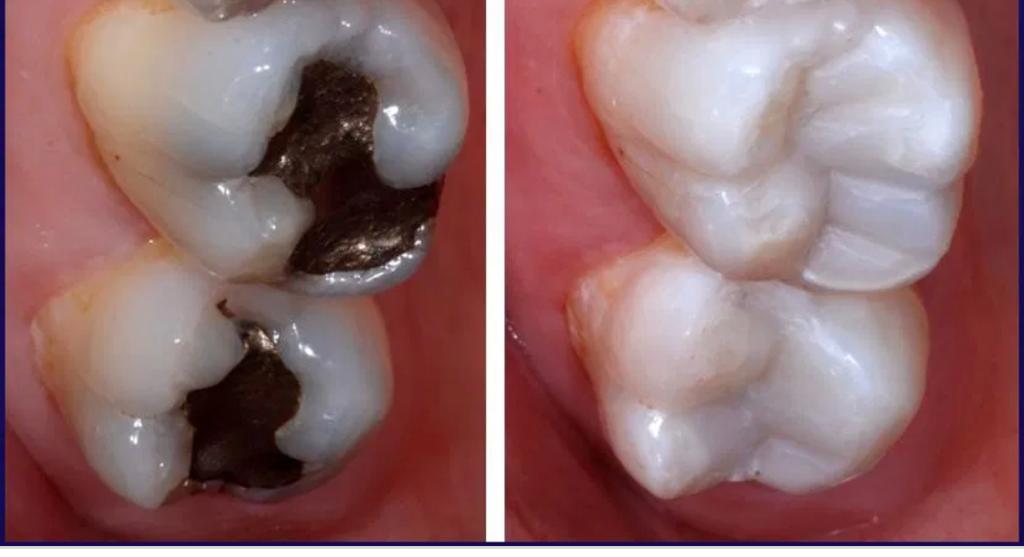
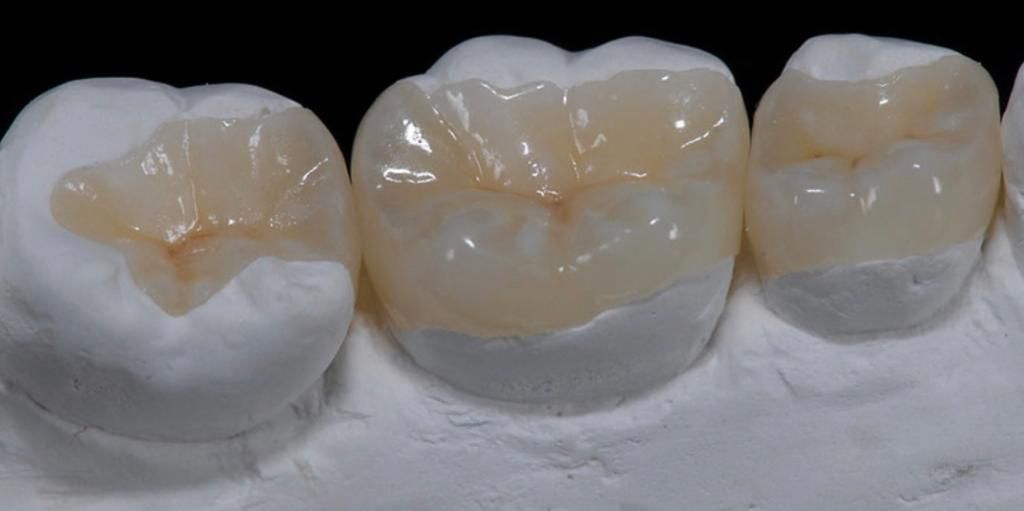
Conservative dentistry is a branch of restorative dentistry, which deals with restoring the integrity of the dental elements even in very critical areas that have lost part of their structure due to multiple factors. It treats the rehabilitation of teeth affected by carious processes, all congenital injuries of the teeth and those caused by trauma such as accidental falls, car accidents or sports injuries. To restore such injuries, a direct or indirect technique can be used. With the direct technique, dentistry prepares a suitable cavity in the tooth, eliminating the diseased or non- conservable tissue, and reconstructs the tooth in the same session; with the indirect technique, the dentist prepares a cavity, eventually makes a pre-reconstruction, and takes an impression which then passes to a dental laboratory. The dental technician who specializes in building artifacts such as dentures, dental prostheses, inlays, then builds a custom-made, high-precision artifact, which will be cemented onto the tooth by the dentist during a subsequent session. Currently, reconstructions of the cavities are carried out with the use of filling materials, such as composite resins and ceramics, which are completely non-toxic and highly aesthetic. There are hardly any more restoration techniques with gold and silver amalgam. Conservative dentistry is based on the concept of minimal invasiveness with the removal of only the carious tissue and its replacement with a restorative material, which is bonded directly to the healthy tissue. However, in the case of excessive loss of dental substance, the filling is not sufficient to restore all the functions of the tooth, so it is necessary to create adhesive restorations with an indirect technique called inlays, which are designed by the dental laboratory. The inlay guarantees greater precision and durability. Fillings are also not recommended in the presence of devitalized teeth. In this case, the best restoration system is the crown (or inlay) which can reduce the risk of fracture that would otherwise be very high for these teeth (especially for premolars, canines, and incisors). Regarding teeth fractured due to trauma, an excellent reconstruction with the highest aesthetic value is the veneer. The inlay offers more advantages than filling, both from the point of view of resistance and from the point of view of the adaptation of the contact points (composite fillings are not always able to be created with the contact points perfectly adhering to the teeth neighbors, with discomfort for the patient, because food residues can stop between the teeth). On small failures, the inlay and filling resistance is similar, but on large restorations the inlay is by far the best solution.
What is tooth decay?
Dental caries is a degenerative disease of the hard tissues of the tooth (enamel and dentin) and its cause is infectious: the infection begins on the surface of the tooth and then proceeds inwards, until it reaches the dental pulp, causing pain and inflammation. Dental caries is caused by bacteria that are none other than the common microorganisms normally present in the oral cavity, usually in the form of bacterial plaque. Therefore, the very first form of caries prevention is careful oral hygiene. The more the caries approaches the pulp tissue, the more bacteria and toxic products can activate very painful and asymptomatic inflammatory processes, such as pulpitis.
What are the symptoms of tooth decay?
Among the most frequent symptoms of caries, we recognize:
- pain in heat and cold;
- pain on chewing;
- pain in the presence of acidic and / or sweet foods;
- intense pain in the presence of pulpitis;
- pain in other adjacent areas of the face.
Since caries cause discomfort only at advanced levels, it often happens that they are neglected, when the affected tooth would need long and complex therapies to be able to be completely rehabilitated.
Caries treatment
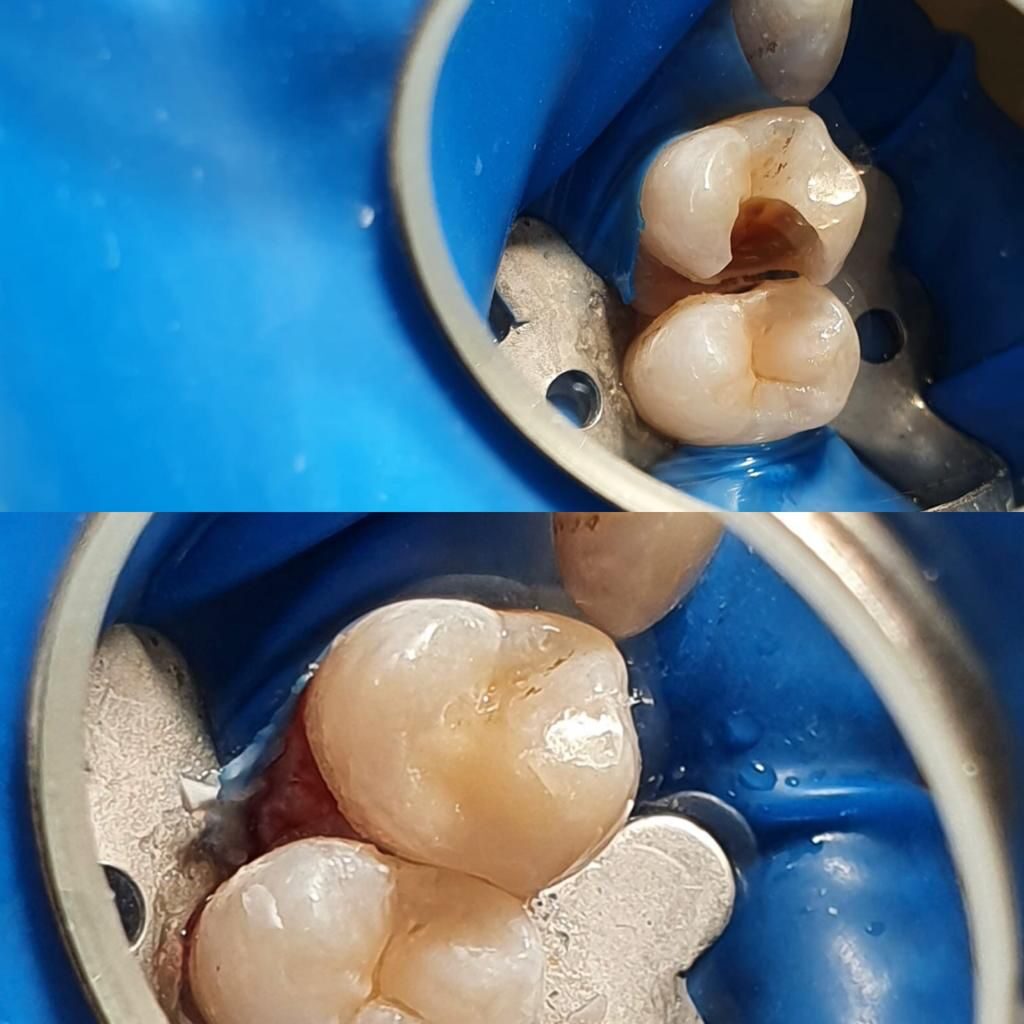
When caries localized in non-visible areas, such as interdental areas or carious relapses developed under old restorations, it is very important to carry out an X-ray examination. In fact, by limiting the diagnosis to visual examination only, part of the carious lesions can escape clinical control. The dentist performs anesthesia and, once the tooth is asleep, isolates the work area with the rubber dam, so that each operation takes place in a clean field, without bacterial contamination. Then, the cavity is prepared by removing the softened and decayed tissue, and the adhesion is carried out which allows to bind the restorative material to the dental structure. We then move on to stratification, which consists in filling the cleaned cavity with composite resin increments. The restoration is modeled to correctly reproduce the anatomy of the tooth and super colors are often used to make the work more natural. Finally, the restored tooth is polished using special burs and rubber pads, to obtain the best possible aesthetic result.
Reconstruction of the dental necks
Sometimes it happens to feel with the tongue like a step between the gum and the tooth. Looking carefully in the mirror, one realizes that one or more dental necks have been uncovered following the retreat of the gum. Depends on what? Is it perhaps the first state of periodontitis? Clearly the answer to this question depends on case to case, for this reason it is always advisable for those with healthy teeth to carry out a professional cleaning every 6 months, with an accompanying check-up. In any case, in the absence of gingival inflammation, a retracted gum, called in technical jargon “gingival recession”, with consequent exposure of a part of the tooth root, can depend, and often and so, on the incorrect use of the toothbrush. Too strong brushing and carried out according to an inadequate technique causes the gum to wear out over time and this irreversible process leads to an increase in dental sensitivity to heat, cold or to foods containing sugars or acid substances, such as lemon citric acid.
To reconstruct the dental collar, you can intervene in two ways:
- bringing the withdrawn gum back to the height it had before it was damaged, making it slide with a surgical intervention;
- using dental veneers for a longer lasting result, capable of giving the best possible aesthetic result.